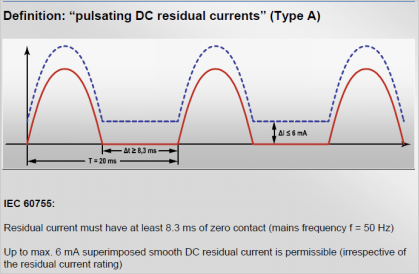
Talking about the Type and Choice of RPCB for Leakage Protection of Distributed Generation System

The properties of copper wire mesh include high electrical conductivity, good thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and malleability. These characteristics make it suitable for various applications:
1. **Electrical Applications**: Copper is an excellent conductor of electricity. Therefore, copper wire mesh is often used in electrical wiring, transformer cores, and as a part of electrical components due to its ability to conduct electric current efficiently.
2. **Heat Exchangers**: The high thermal conductivity of copper wire mesh makes it useful in heat exchangers where it can help transfer heat from one medium to another.
3. **Filtering**: Copper wire mesh can be used as a filter in various industries, such as in the food industry to filter out impurities from liquids or in water treatment plants to remove particulate matter.
4. **Industrial Coatings**: Copper wire mesh is sometimes used in industrial coatings for its anti-corrosive properties.
5. **Architectural Applications**: In modern architecture, copper wire mesh can be used for decorative purposes, offering both aesthetic appeal and functional benefits like sun shading or acoustic management.
6. **Art and Craft**: Due to its malleability and aesthetic qualities, copper wire mesh is also used in artistic creations and crafts.
When selecting copper wire mesh, factors like the gauge (thickness), weave pattern, and the specific application should be considered to ensure the right product is chosen.
Copper Wire Mesh,Copper Wire Mesh Screen,Yellow Copper Mesh Rolls,Copper RFI Shielding Mesh
Hebei Yingkang Wire Mesh Product Co.Ltd , https://www.wiremesh-china.com
