Comprehensive Guide to Amada Press Brake
Amada Corporation, established in 1946, is a globally renowned manufacturer of metalworking machinery. Headquartered in Japan, the company holds a significant market share in the global metalworking machinery industry, with numerous awards for innovation and quality. Amada specializes in providing high-quality sheet metal processing equipment, including laser cutting machines, press brakes, turret punch presses, and automated systems. Amada's dedication to innovation and quality has positioned it as a leader in the sheet metal fabrication industry, with a strong global presence across Asia, Europe, and the Americas. Apart from Amada, ADH Machine Tool is also making a name for itself in the global market. This Chinese manufacturer focuses on providing CNC, NC, tandem, and electric press brakes, winning numerous customers' favor with customized options and strong after-sales support. ADH's products are characterized by high cost-performance, making them an important choice for many small and medium-sized enterprises. The origins of the Amada press brake machine trace back to 1955 through Promecam, a French company known for its pioneering work in press brake technology. In 1986, Amada acquired Promecam, integrating their advanced European technologies into Amada's expanding portfolio. This acquisition marked the beginning of a new era, setting the stage for continuous innovation in press brake technology. Similar to Amada's integration of European technology, ADH Machine Tool has actively absorbed international advanced technology over the past decade, continuously optimizing its CNC control systems and hydraulic design. Through technological accumulation, ADH has successfully launched various products that meet high-precision bending requirements. During the 1960s to 1990s, Amada built upon the foundation laid by Promecam, gradually enhancing their press brake designs. The integration of hydraulic systems during this period significantly improved the precision and efficiency of metal bending operations. Although specific innovations from this era are less documented, it was a time of steady growth and refinement in press brake technology. The 2000s marked a significant leap in Amada's press brake technology, characterized by the introduction of servo-hydraulic and hybrid systems. These advancements brought about improved energy efficiency and performance. Building on the technological advancements of the 2000s, the 2010s saw the introduction of several models that focused on automation and improving the user experience: In recent years, Amada has continued to push the boundaries of press brake technology with the introduction of the HRB series and other advanced models: Amada bending machine tools are equipped with various advanced drive systems that enhance performance and precision: In addition to Amada's servo-hydraulic system, ADH Machine Tool's servo-electric press brakes are also popular for their high efficiency and energy savings. ADH's electric press brakes use advanced CNC control technology, helping customers reduce energy consumption by more than 50%, making them ideal for companies that value sustainable development. Automatic tool changers are a standout feature in many Amada machines, significantly enhancing productivity: The ATC system allows for quick and precise tool changes without manual intervention, making it ideal for high-mix, low-volume production environments. ADH Machine Tool's CNC press brakes also integrate quick tool-change systems, ensuring minimal downtime and enabling high-mix, low-volume production environments—comparable to Amada’s ATC-equipped models. These press brakes are designed to deliver high precision and accuracy in metal bending: Amada bending machines prioritize operator comfort and ease of use: Amada bending machines are engineered to be energy-efficient and environmentally friendly: Amada machine tools offer a high degree of versatility and can be customized to meet specific production needs: Amada integrates advanced software solutions and automation technologies to streamline bending operations: Safety is a crucial aspect of press brakes, with several models featuring advanced safety systems: Amada press brakes are known for their advanced drive systems, automation capabilities, and high precision, making them a popular choice in industries requiring efficient and accurate metal bending. With features such as servo-hydraulic systems, automatic tool changers, and IoT-enabled software, Amada offers comprehensive solutions that enhance productivity and operational efficiency. On the other hand, ADH Machine Tool, a prominent Chinese manufacturer, provides a versatile range of press brakes, including CNC, NC, tandem, and electric models, focusing on affordability, customization, and strong after-sales support. To provide a clearer understanding of the strengths and differences between these two manufacturers, the following table offers a detailed comparison of their key features and capabilities. Amada Corporation offers a diverse range of press brake models, each tailored to meet specific manufacturing requirements. These models are renowned for their precision, efficiency, and advanced technological features. The HFE 3i series is known for its user-friendly interface and precise bending capabilities. This series includes advanced features that improve both productivity and accuracy in metal forming. Industry Applications: Ideal for automotive, aerospace, and general metal fabrication industries where precision and efficiency are paramount. Building on the precision and user-friendliness of the HFE 3i series, the HRB series introduces additional robustness and versatility. This series emphasizes precision and productivity, catering to both high-volume and custom manufacturing needs. Industry Applications: Suited for heavy machinery, shipbuilding, and construction industries that require robust and versatile bending solutions. The HG ATC series incorporates automatic tool changers and hydraulic crowning systems, making it ideal for high-mix, low-volume production environments. This series is designed to minimize setup times and maximize operational efficiency. Industry Applications: Perfect for job shops and custom metal fabricators that need to switch between different jobs quickly and efficiently. The EGB-ATCe series features servo-electric technology, offering energy efficiency and high performance. This series is designed for manufacturers seeking eco-friendly solutions without compromising on precision and productivity. Industry Applications: Ideal for electronics, medical device manufacturing, and other industries prioritizing energy efficiency and precision. The HFE M2 EVO series is designed with an emphasis on ergonomic features and advanced control systems. This series is particularly suitable for small parts bending and offers high precision and flexibility. Industry Applications: Best suited for precision parts manufacturing, including electronics and small appliance industries. The HD 1003 ATC model stands out for its automatic tool changer and advanced bending capabilities. This model is designed to handle complex bending tasks with high precision and efficiency. Industry Applications: Suitable for precision engineering, automotive component manufacturing, and other high-precision industries. The HG-RM series features robotic integration for automated bending operations. This series is designed for manufacturers looking to enhance productivity through automation. Industry Applications: Ideal for large-scale manufacturing environments such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery industries where automation can significantly boost productivity. In addition to Amada's multiple series of press brakes, ADH Machine Tool also offers a diverse range of models to meet different customer needs. Their products include CNC and NC series, with bending forces ranging from 40 tons to 600 tons and bending lengths up to 6 meters. ADH's tandem press brakes are especially suitable for processing large structural components and support efficient automatic control. Amada press brakes are at the forefront of metalworking technology, incorporating several advanced features and innovations that enhance productivity, precision, and efficiency. These technologies are particularly beneficial in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery, where precision and efficiency are crucial. Amada's integration of servo-hydraulic systems combines the power of hydraulic systems with the precision of servo motors, making them ideal for industries like automotive and aerospace. This hybrid approach allows for: For example, the HFE M2 EVO series utilizes servo-hydraulic technology to achieve high precision in bending operations while conserving energy. The Virtual Prototype Simulation System (VPSS) is an advanced software solution designed to streamline the programming and simulation of bending operations. VPSS allows operators to: For instance, a leading automotive manufacturer reduced their setup times by 30% using VPSS, illustrating its impact on production efficiency. The AMNC 3i controller is a state-of-the-art control system that offers a user-friendly interface with touchscreen capabilities. Key benefits include: This advanced control system is featured in several press brake models, including the HRB and HG ATC series. Did you know that Amada's advanced laser safety systems not only protect operators but also maintain high productivity by minimizing manual safety checks? These systems use laser sensors to: The integration of laser safety systems enhances workplace safety while allowing for faster and more efficient bending operations. Amada integrates IoT connectivity and smart manufacturing into their press brakes, embracing Industry 4.0 principles to enhance real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. IoT-enabled press brakes can: Automatic tool changers (ATC) are a hallmark of Amada's innovative press brake technology. These systems allow for: The ATC system is particularly beneficial for high-mix, low-volume production environments where frequent tool changes are required. Models like the HD ATC and HG ATC series are equipped with automatic tool changers, enabling manufacturers to switch between different bending operations quickly and efficiently. Amada's advanced software solutions, such as Dr. ABE Bend, further enhance the capabilities of their press brakes. Dr. ABE Bend automates the programming of bending operations, providing: By integrating advanced software solutions with their press brake models, Amada enables manufacturers to achieve higher levels of precision and efficiency in their metal forming operations. Amada press brakes can be integrated with robotic systems for automated material handling, reducing manual intervention and increasing throughput. Robotic integration allows for: This technology is particularly beneficial for large-scale manufacturing environments where high volumes of parts need to be produced with minimal variation. The HG-RM series, for example, features robotic integration, making it ideal for industries such as automotive and aerospace. Servo-electric technology is another innovation that sets Amada press brakes apart. This technology uses electric servos instead of hydraulic systems, offering several advantages: For example, Amada's servo-electric technology can reduce energy consumption by up to 50% compared to traditional systems. Servo-electric press brakes, such as the EGB-ATCe series, provide high precision and performance while minimizing their ecological footprint. This makes them an excellent choice for manufacturers seeking eco-friendly solutions without compromising on quality. With the basic functions verified, we can now delve deeper into the electrical components to ensure they are in optimal condition. Once electrical components are verified, it's essential to turn our attention to the hydraulic system, which plays a critical role in the press brake's operation. Hydraulic systems are critical components of many Amada press brakes. Common hydraulic problems include: Electrical problems can disrupt the normal operation of Amada press brakes. Key issues include: Proper tooling alignment is crucial for accurate bending operations. Common problems include: ADH's CNC press brake is equipped with an intelligent adjustment system that can automatically detect and correct alignment errors, reducing the operator's workload. Meanwhile, its durable mold material extends service life and reduces replacement frequency. The back gauge positions the metal sheet for bending, and its inaccuracy can lead to errors. Address these issues by: Ram tilt occurs when the press brake's ram is not parallel to the bed, resulting in uneven bends. To resolve this: Excessive material deformation or springback can occur due to improper bending parameters. To mitigate this: Surface imperfections and tool sticking can affect the quality of bends. Address these by: Regular maintenance is essential for preventing many common issues with Amada press brakes. Key practices include: By addressing these common issues through thorough troubleshooting and regular maintenance, operators can ensure the optimal performance and longevity of their Amada press brakes. Accessing maintenance passwords for Amada press brakes is essential for performing advanced diagnostics, maintenance, and troubleshooting. These passwords are protected to ensure only qualified personnel can make critical adjustments to the machine. Follow these steps and best practices to access and manage these passwords effectively. After contacting Amada Technical Support, the next step is to enter maintenance mode using the provided password. With access to the maintenance passwords secured, it’s important to follow best practices to manage them effectively. By following these steps and best practices, operators can securely access and manage maintenance passwords for Amada press brakes, ensuring advanced diagnostics and maintenance tasks are performed safely and effectively. When purchasing an Amada press brake, several critical factors must be evaluated to ensure the machine meets your manufacturing needs: For businesses with limited budgets, purchasing new equipment from ADH Machine Tool can be a wise choice. ADH's new products are not only more affordable but also come with comprehensive after-sales support and customized services, helping clients avoid the potential risks of second-hand machines. Purchasing through Amada's network of authorized dealers and distributors ensures you receive genuine products and reliable support. These dealers offer various services, including installation, training, and maintenance. Online marketplaces and machinery websites are excellent resources for finding both new and used Amada press brakes. These platforms often feature detailed listings with specifications, prices, and seller information. Attending trade shows and exhibitions allows you to see Amada press brakes in action and speak directly with company representatives. Automatic Glue Turning Machine Stainless steel flipping machine,Mirror fully automatic glue flipping machine,Mirror stainless steel flipping machine Dongguan Zhenggong Electromechanical Equipment Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.mixer-cn.comI. Introduction to Amada Press Brake
II. Evolution of Amada Press Brakes
Early Beginnings
1960s-1990s: Foundation and Growth
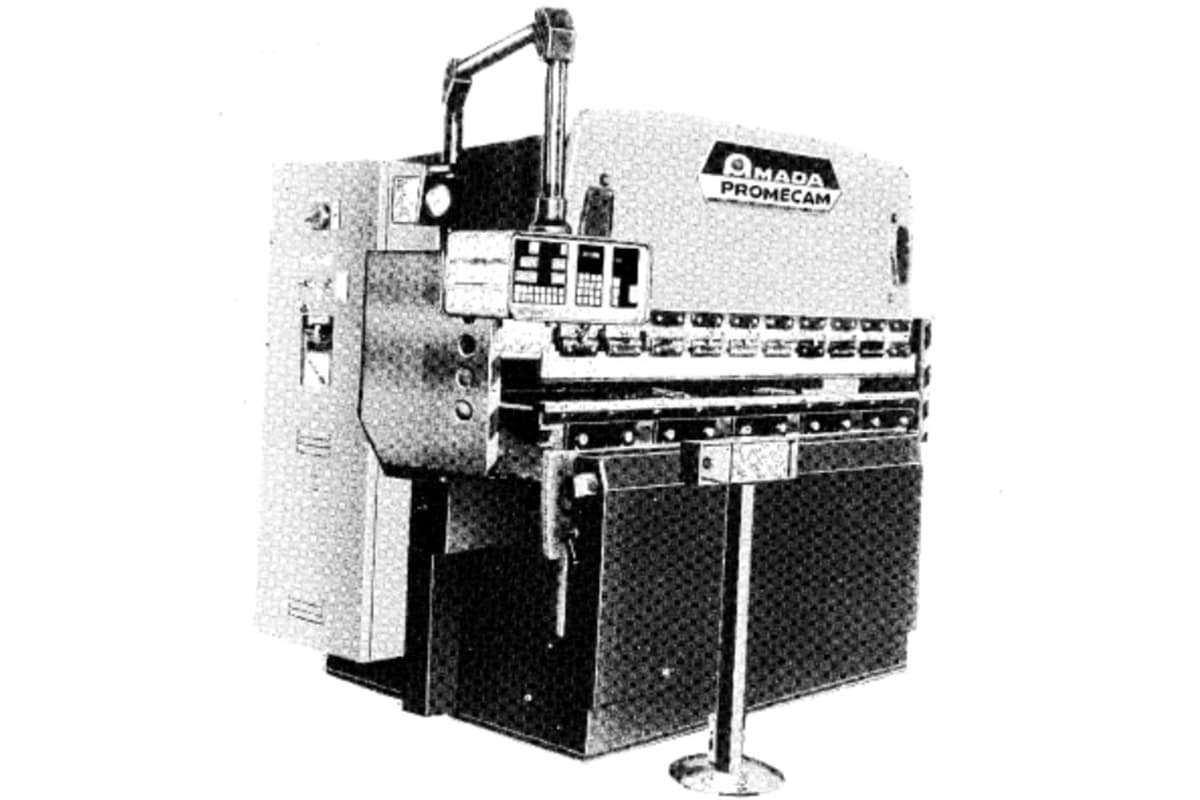

2000s: Technological Advancements
HD Series
HFE M2
HD ATC
2010s: Automation and User Experience
HG ATC Series
HFE 3i Series
HFE M2 EVO
2020s: Cutting-Edge Innovations
HRB Series
HRB ATC
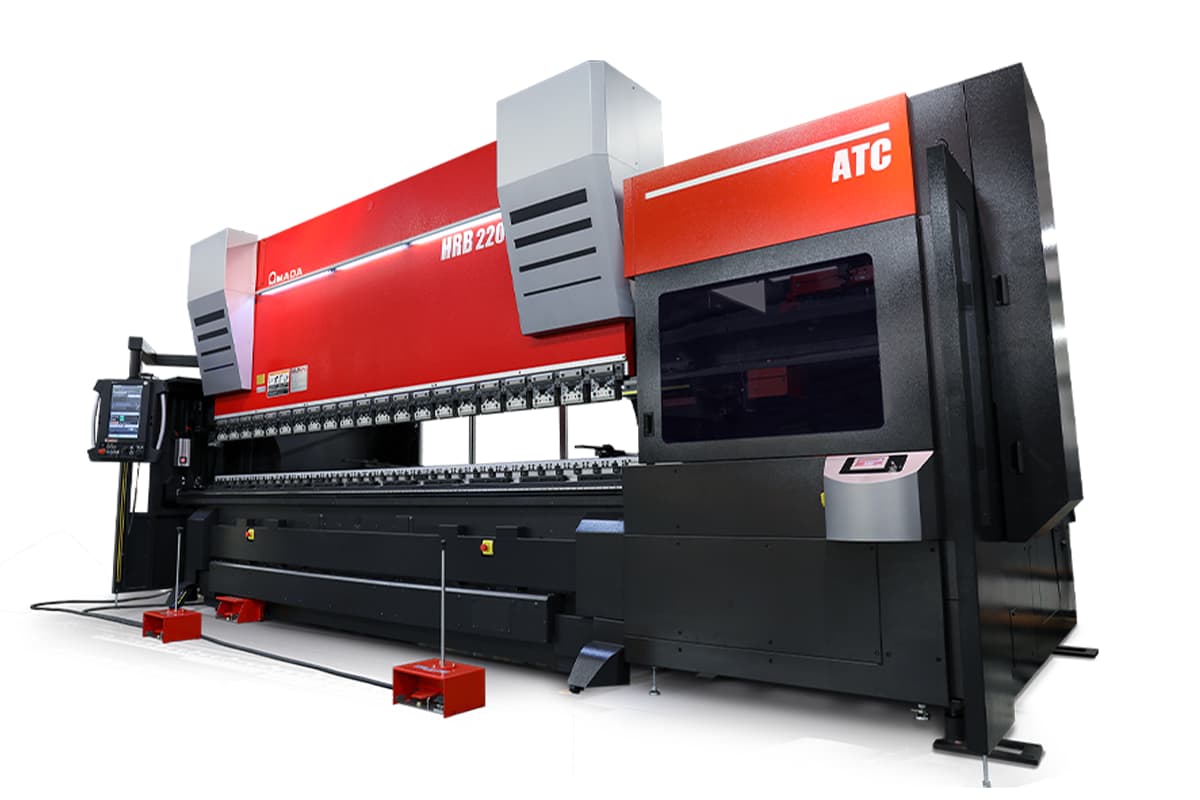

EGB-ATCe
III. Key Features of Amada Press Brakes
Advanced Drive Systems
Automatic Tool Changers (ATC)
Precision and Accuracy
Ergonomics and User-Friendly Controls
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Friendliness
Versatility and Customization
Advanced Software and Automation
Safety and Stability
Comparison with ADH Press Brake
Feature ADH Machine Tool Amada Drive System Electro-hydraulic and servo-electric options available; hybrid options for energy savings. Servo-hydraulic, hydraulic, and servo-electric systems, optimizing precision and energy efficiency. Automation Offers CNC models with advanced programming for increased precision and productivity; supports bending cells for unmanned operation. Includes automatic tool changers (ATC) to minimize setup time; integrated robotics for material handling. Precision Control Equipped with advanced CNC controllers (DELEM, ESA, CYBELEC); offers crowning systems to enhance accuracy. Uses AMNC 3i controller and Bi-S technology to ensure high precision and automatic thickness adjustment. Energy Efficiency Electric models reduce power consumption, aligning with sustainability goals. Servo-electric models focus on lowering environmental impact and noise. Customization & Versatility Supports multiple configurations like tandem and large-scale models for heavy-duty applications. Offers multi-axis backgauges for customized bending operations and IoT connectivity for real-time monitoring. Software and Connectivity Features integration with industry-standard CNC controllers for easy programming. Provides Dr. A Bend software for automation and IoT-enabled connectivity for maintenance and optimization. Safety Features Includes safety curtains, emergency stops, and intelligent clamping systems. Utilizes laser safety systems and robotic automation for safe operations. Warranty & Support Offers 15-year structural and 2-year accessory warranties; 24/7 technical support. Emphasizes quick support and replacement services to minimize downtime. IV. Popular Models and Their Specifications
HFE 3i Series
HRB Series
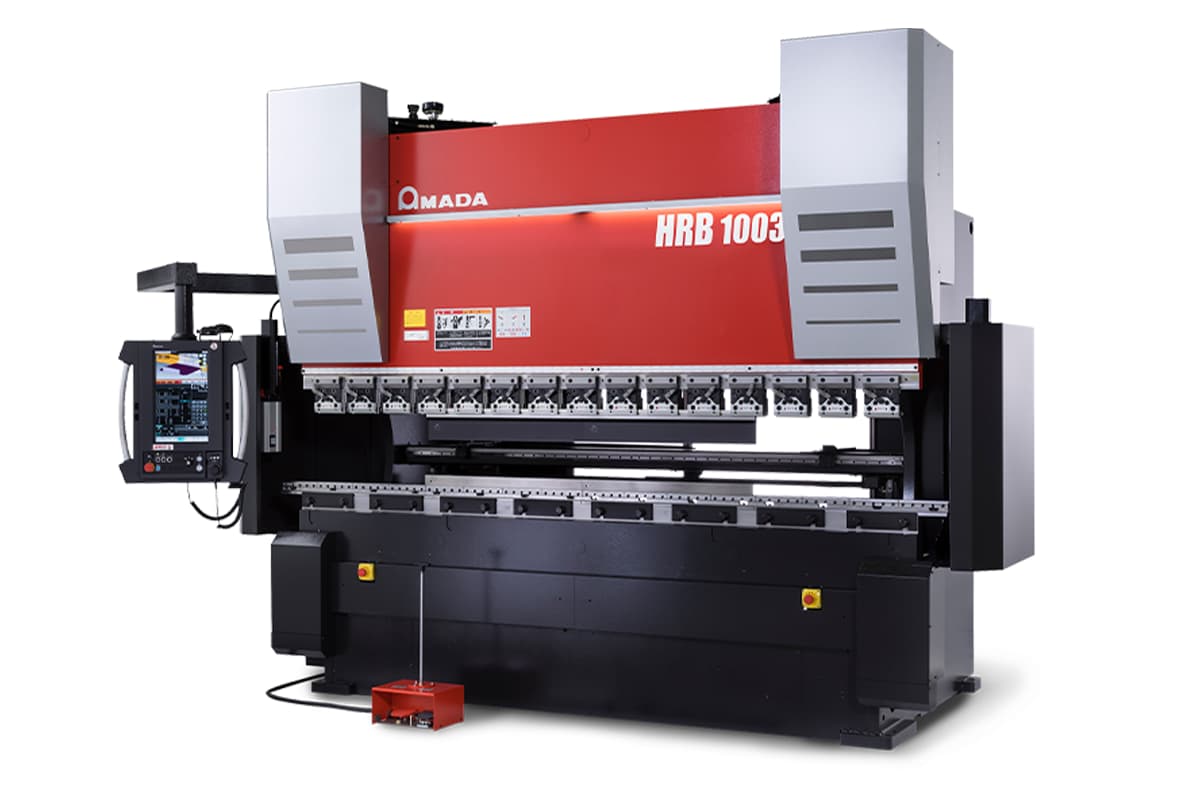

HG ATC Series
EGB-ATCe Series
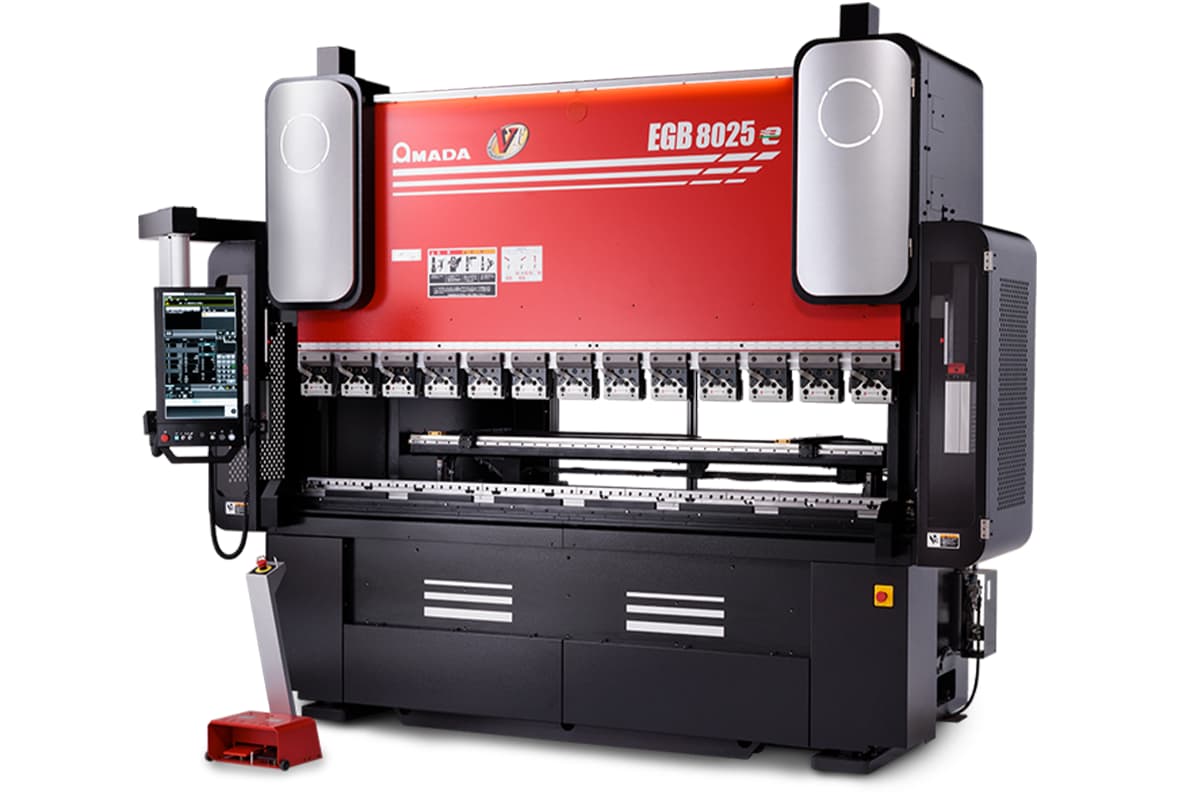

HFE M2 EVO
HD 1003 ATC
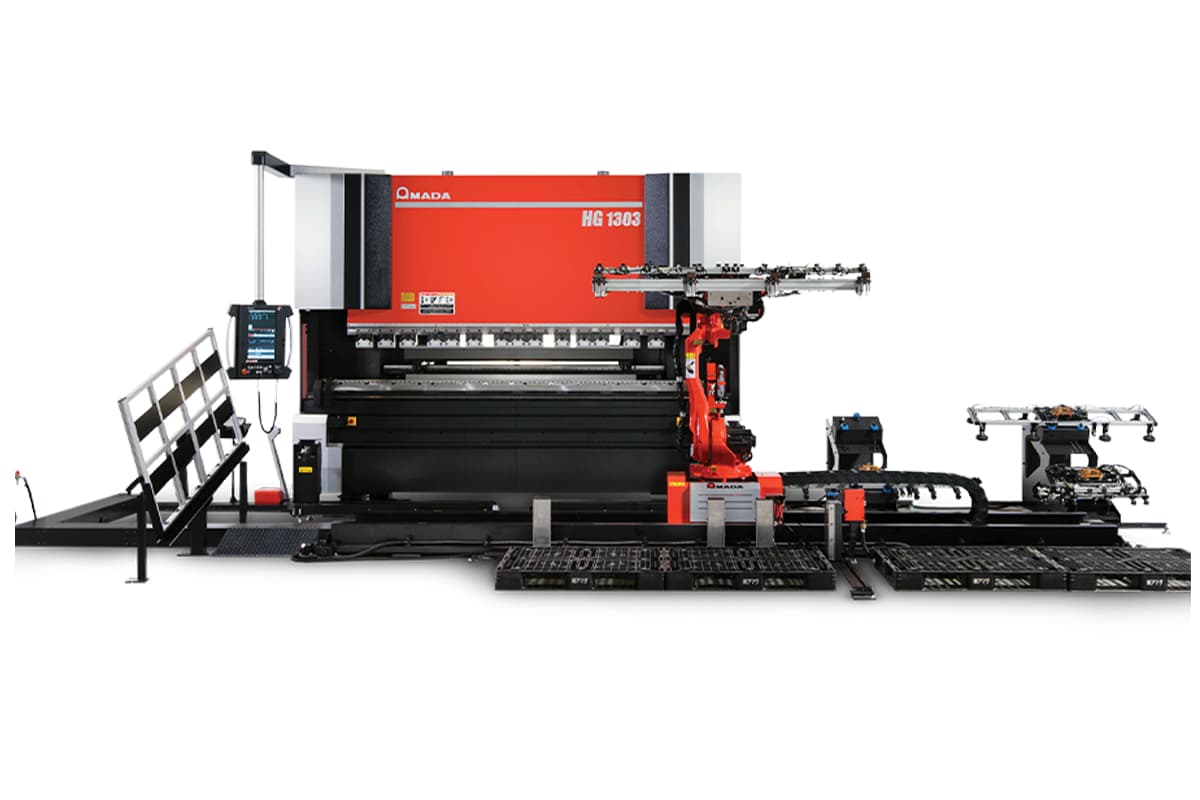
HG-RM Series

V. Advanced Technologies and Innovations
Servo-Hydraulic Systems
Virtual Prototype Simulation System (VPSS)
AMNC 3i Controller
Laser Safety Systems
IoT Connectivity and Smart Manufacturing
Automatic Tool Changers (ATC)

Advanced Software Solutions
Robotic Integration
Servo-Electric Technology
VI. Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide for Amada Press Brake
Identify the Problem
Check Basic Functions
Inspect Electrical Components
Examine Hydraulic System
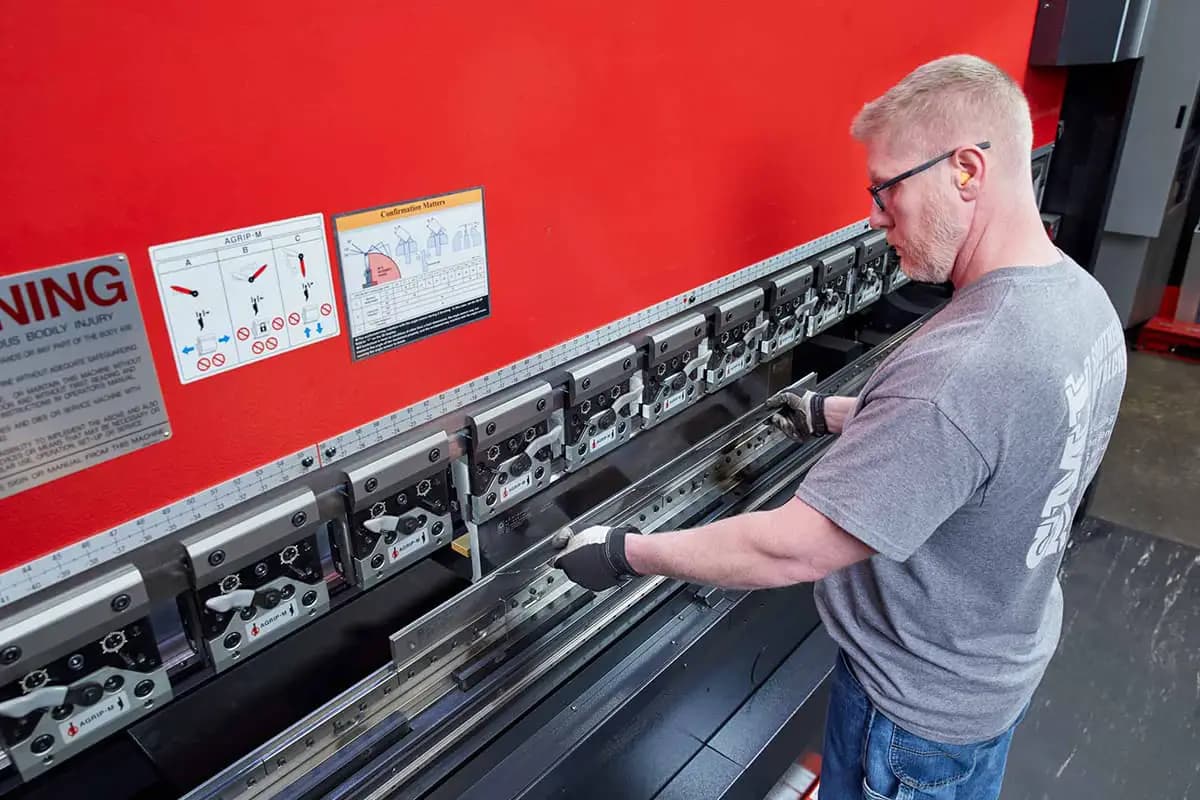
Align and Inspect Tooling

Consult the Manual
Advanced Diagnostics
Implement Solutions
Verify the Solution
VII. Common Issues with Amada Press Brakes
Hydraulic System Problems
Electrical Issues
Tooling Alignment and Wear
Back Gauge Inaccuracy
Step-by-Step Back Gauge Calibration Guide
Ram Tilt Issues
Material Deformation and Springback
Surface Imperfections and Tool Sticking
Maintenance and Regular Checks
How to Access Maintenance Passwords for Amada Press Brakes
Contacting Amada Technical Support
Steps to Use Maintenance Passwords for Amada Press Brakes
Best Practices for Managing Maintenance Passwords
Troubleshooting Password Issues
VIII. Factors to Consider When Buying an Amada Press Brake

Bending Force and Capacity
Bending Length
Control Systems and Automation
Energy Efficiency
Budget and Financing Options
New vs. Used Amada Press Brakes
New Press Brakes
Used Press Brakes
Understanding Pricing and Financing Options
Pricing Factors
Financing Options
Where to Buy Amada Press Brakes
Popular Models and Key Features
Online Marketplaces and Machinery Websites
Trade Shows and Exhibitions
